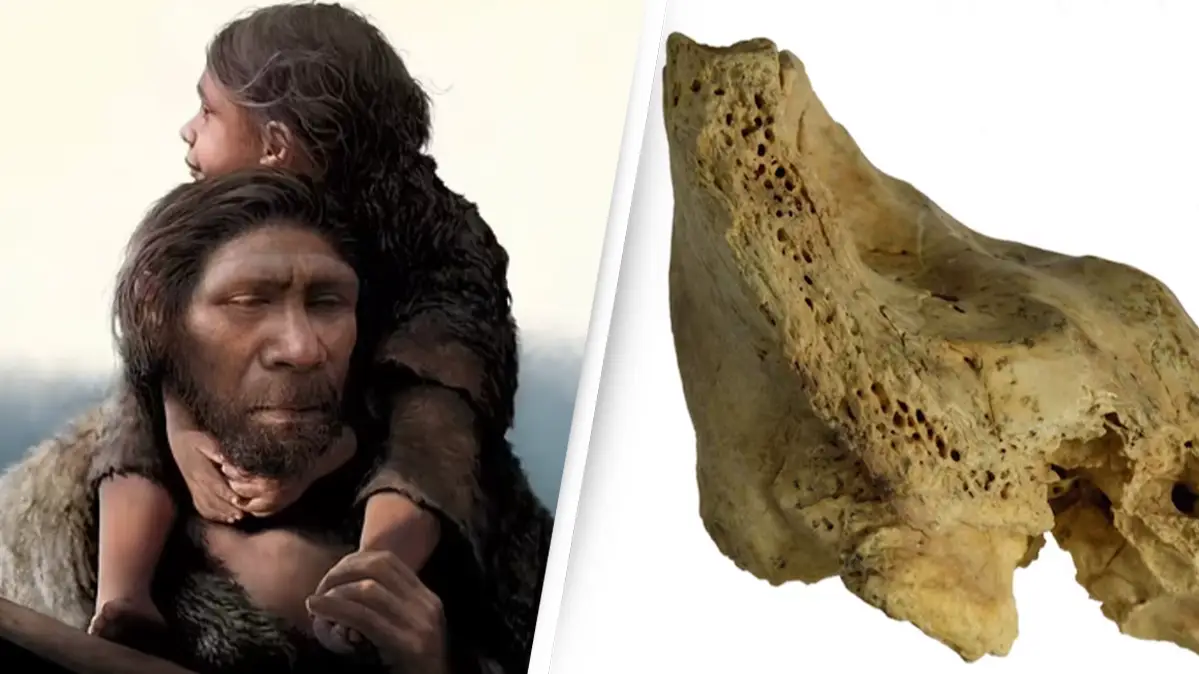

Scientists have uncovered a skull fragment in Spain believed to be the earliest-known evidence of Down syndrome.
Researchers have been working to analyze an of ancient fossil, thought to be from a six-year-old child who lived more than 145,000 years ago.
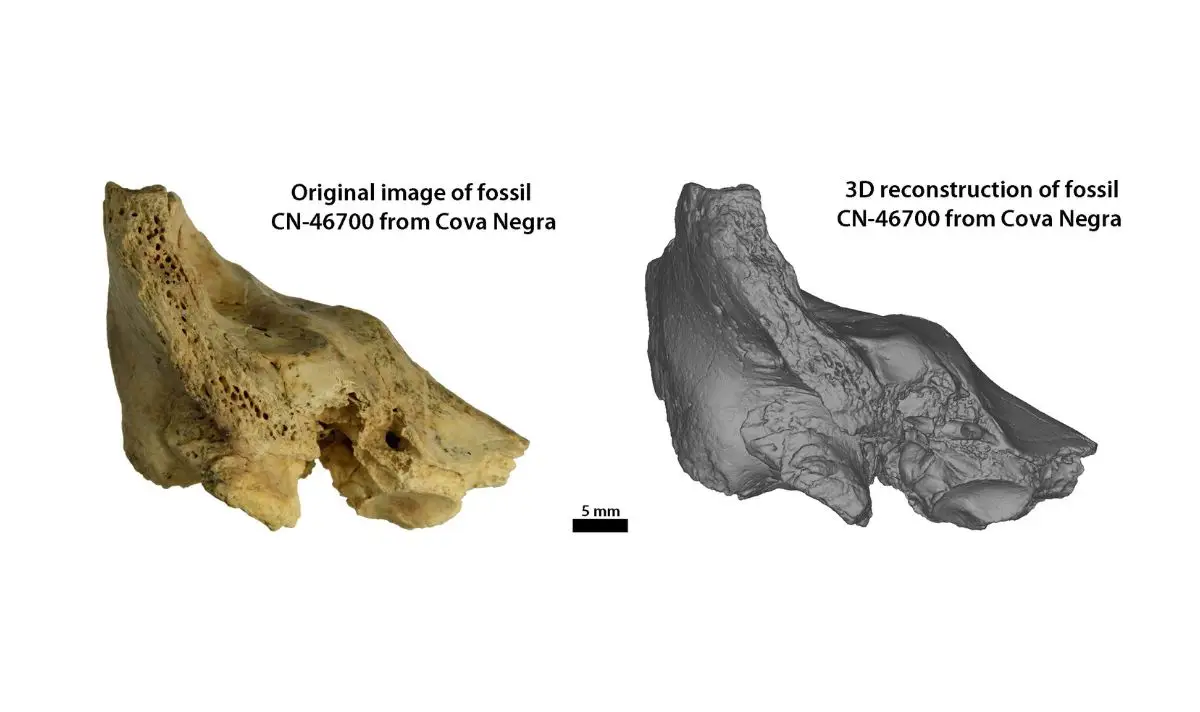
The small cranial fragment in question was one of three relics initially found in 1989 after experts completed a dig at the Cova Negra archaeological site in the province of Valencia, Spain.
Advert
However, through new research efforts, experts believe the Neanderthal - dubbed ‘Tina’ - may have suffered from a congenital pathology in the inner ear that likely caused severe hearing loss, an inability to maintain balance and disabling vertigo.
Moreover, the scientists say that Tina’s community may have provided altruistic care and supported the young child since they survived many years after birth.
Speaking about the new findings, published in the Science Advances journal, study lead author Dr Mercedes Conde-Valverde, an anthropologist at University of Alcalá, said: “Until now, it was only possible to diagnose Down syndrome in fossil specimens through the analysis of ancient DNA.”
She continued to tell the Daily Mail that the group has finally been able to ‘diagnose it through an anatomical study of the inner ear’.
Dr Conde-Valverde added: “This opens up the possibility of studying the potential presence of Down syndrome in fossil specimens and thus being able to document its prevalence in past populations.”
On the topic of altruistic care, she explained: "All known cases of care [in Neanderthals before now] involved adult individuals, leading some scientists to believe that this behaviour was not genuine altruism, but merely an exchange of assistance between equals."
“The survival of this child, beyond the period of breastfeeding, implies group caregiving, probably more extended than parental caregiving, typical of a highly collaborative social context among the members of the group,” added study co-author Valentín Villaverde, a University of Valencia emeritus professor of prehistory.
To come up with the recent findings, researchers analysed the ‘an immature temporal bone’ found in 1989 and used micro-computed tomography to see inside the object.
A digital scan of the temporal bone showed a combination of inner ear abnormalities consistent with Down syndrome, as per the study.
Furthermore, the fossil showed a reduced volume in the cochlear - a fluid-filled, spiral-shaped cavity found in the inner ear.
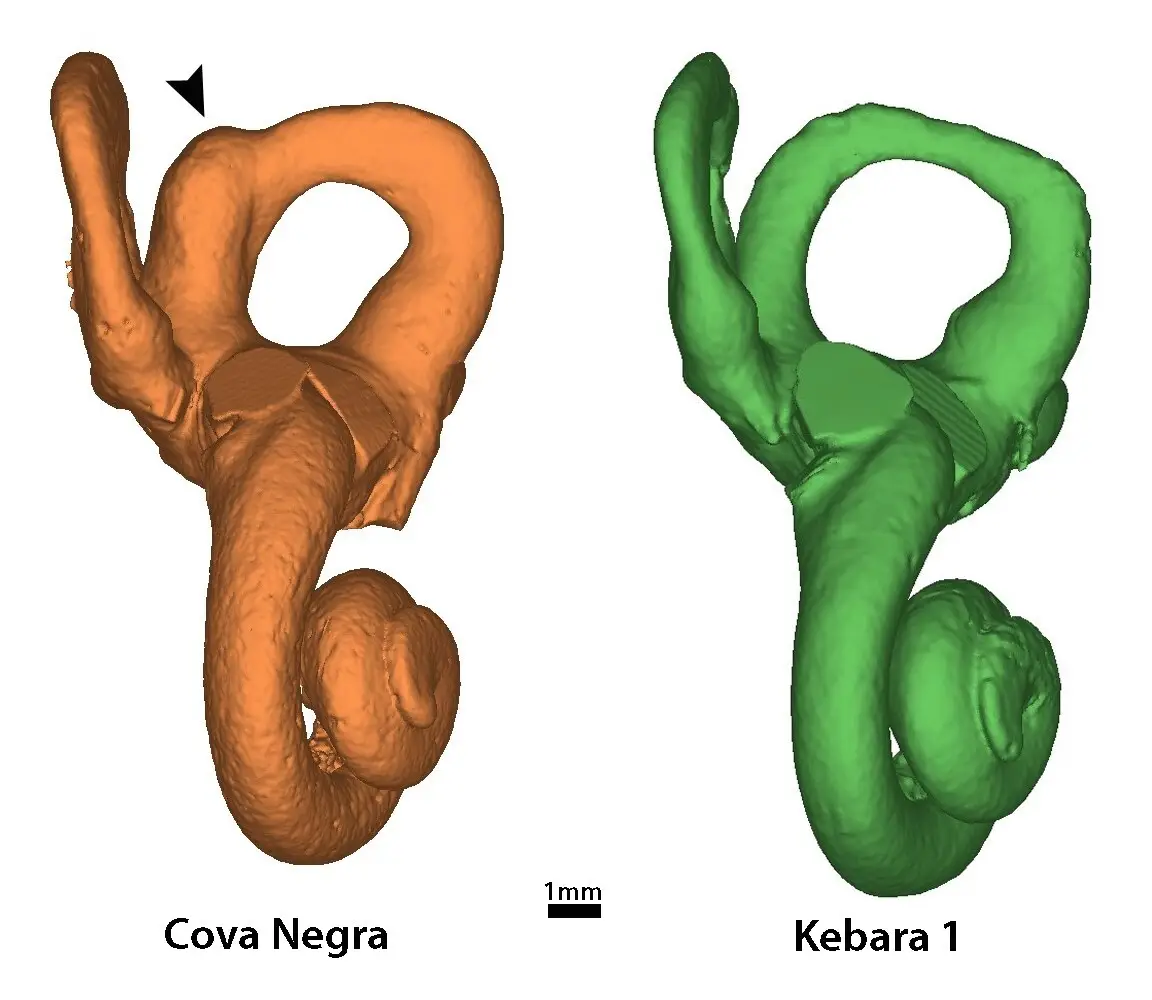
The study suggests therefore that Tina’s cavity was much narrower than the average Neanderthals and therefore exhibits a similar cochlear volume found in 50 percent of children with Down syndrome.
Following the publication of the study, Dr Conde-Valverde said: “The discovery of Tina represents the oldest known case of Down syndrome and demonstrates that the diversity observed in modern humans was already present in prehistoric times.
“This finding ensures that the story of human evolution includes us all.”
While the fossil’s precise age has yet to be determined, the study participants believe the relic from the Cova Negra site is around 273,000 and 146,000 years old.
