
Stargazers are in for a treat as a 'once-in-a-lifetime event' could be set to illuminate the night sky over North America.
Yes, Canadians and Americans may witness a star exploding around 3,000 light years away, which is part of a two-star system that are in orbit of each other.
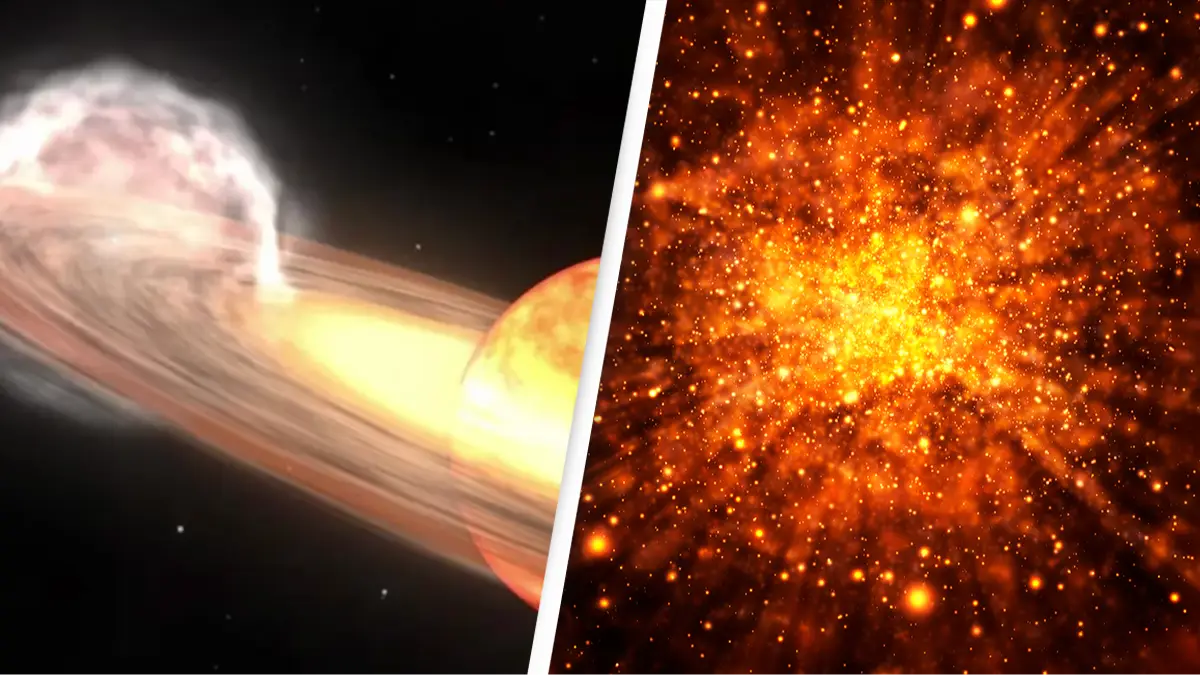
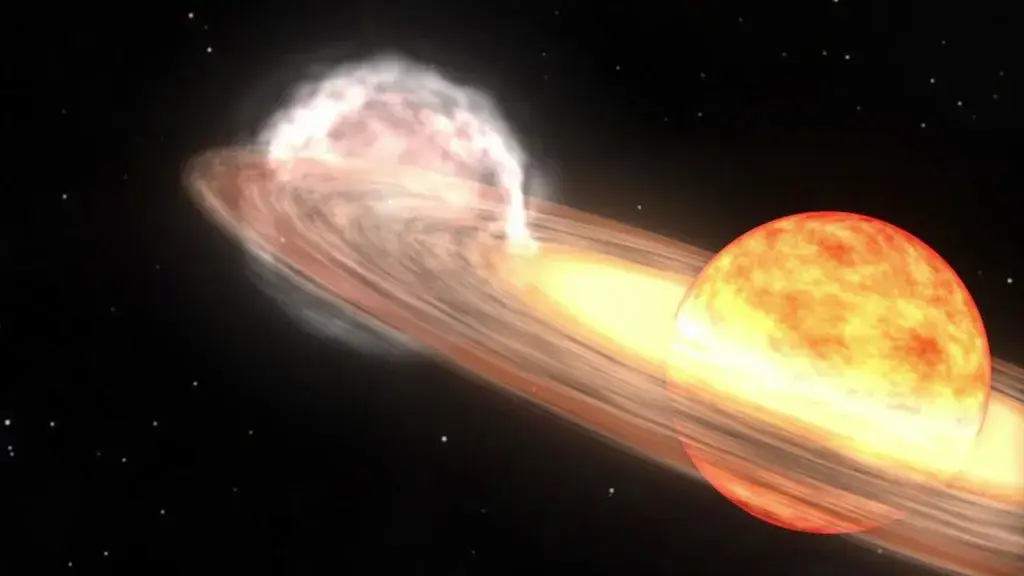
The system, which has been named T Coronea Borealis, or 'T CrB' for short, consists of a red giant star and a white dwarf star.
Advert
They are both in different stages of a star's life cycle - red giants are large and in their final stages while white dwarfs are small and are slowly cooling after exhausting their nuclear fuel - the process takes billions of years.
For years, the white dwarf has been absorbing the red giant's hydrogen and due to a build up of material on its surface it has come under increasingly more pressure and heat - which results in a thermonuclear explosion.
For the T CrB, also known as 'Blaze Star', the event happens every 80 years according to NASA, but it shouldn't be mistaken for a supernova - which happens when the star itself explodes.
It will be a nova event and it will just be the buildup on the surface that explodes. Despite being so far away, it would take around 57 million years to travel to if you were flying through space at 35,000mph. The explosion is also set to be so incredibly ginormous that it will be visible from Earth.
How astronomers and physicists like Brian Cox know all this about our planet is completely beyond me, the science behind it all is incredible.

Dr Rebekah Hounsell, an assistant research scientist specialising in nova events at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, spoke about the event.
She said: “It’s a once-in-a-lifetime event that will create a lot of new astronomers out there, giving young people a cosmic event they can observe for themselves, ask their own questions, and collect their own data.
“It’ll fuel the next generation of scientists.”
So, how can we see it and when will it take place?
Unfortunately, astronomers can only make an educated guess as to when it will happen, and they believe it will occur by the end of this month - so likely this week.
But to be able to see it you'll need to know where to look - and you'll have to find the 'Northern Crown' where the star system sits - but until the eruption, it won't be visible.
A diagram of how to find the Northern Crown can be seen below which appears as a horseshoe beside 'Corona Borealis'.
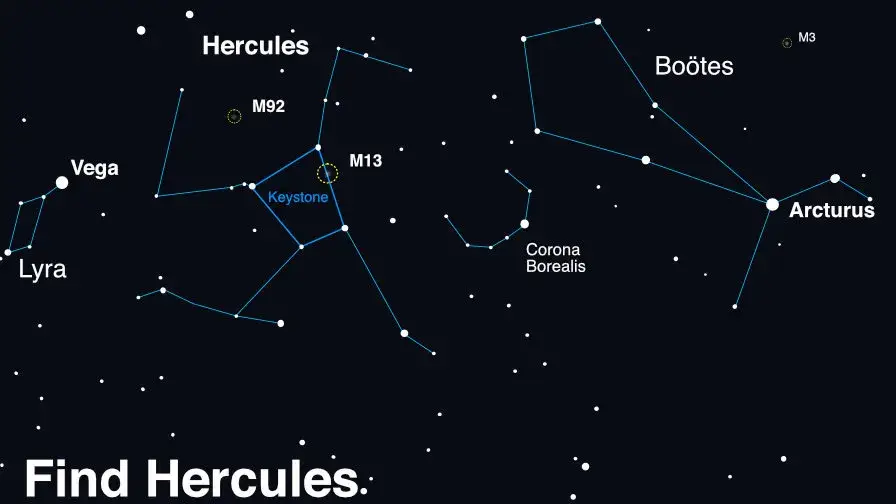
Once it finally erupts, it will be visible to the naked eye for a little less than a week, NASA confirm.
Hounsell added: “There are a few recurrent novae with very short cycles, but typically, we don’t often see a repeated outburst in a human lifetime, and rarely one so relatively close to our own system.
"It’s incredibly exciting to have this front-row seat.”